
In modern web development, microservices have gained immense popularity due to their scalability, flexibility, and maintainability. NestJS, a progressive Node.js framework, provides excellent support for building microservices efficiently. In this blog, we will explore how to use NestJS to build and manage microservices effectively.
Why NestJS for Microservices?
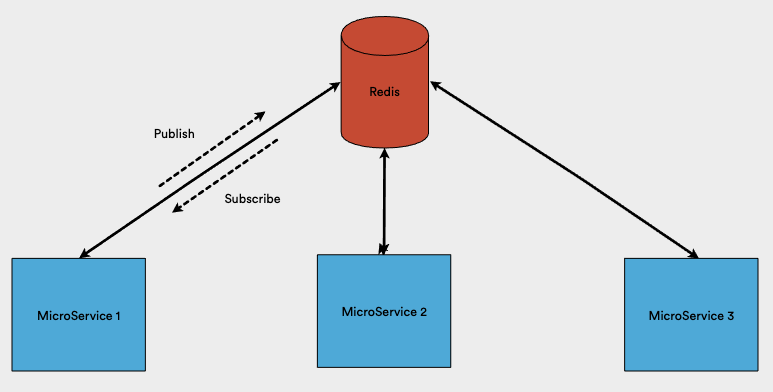
- Built-in support for microservices via different transport layers like TCP, Redis, Kafka, and NATS.
- Dependency Injection for better service management.
- Scalability with modular architecture.
- Powerful decorators and metadata reflection for seamless development.
Setting Up a NestJS Microservices Architecture
1. Install NestJS CLI
npm install -g @nestjs/cli2. Create a New Microservice
nest new microservice-app cd microservice-app nest g app user-service3. Implement a Microservice
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { MicroserviceOptions, Transport } from '@nestjs/microservices';
import { UserModule } from './user.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.createMicroservice<MicroserviceOptions>(UserModule, {
transport: Transport.TCP,
options: { port: 3001 },
});
await app.listen();
console.log('User microservice is running on port 3001');
}
bootstrap();4. Create a Service to Handle Requests
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { MessagePattern } from '@nestjs/microservices';
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
private users = [{ id: 1, name: 'John Doe' }];
@MessagePattern({ cmd: 'get_users' })
getUsers() {
return this.users;
}
}5. Create a Client Gateway
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import { ClientProxyFactory, Transport } from '@nestjs/microservices';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
const client = ClientProxyFactory.create({
transport: Transport.TCP,
options: { host: 'localhost', port: 3001 },
});
await app.startAllMicroservices();
await app.listen(3000);
console.log('Main application is running on port 3000');
const users = await client.send({ cmd: 'get_users' }, {}).toPromise();
console.log(users);
}
bootstrap();
Scaling with Different Transport Strategies
- TCP (default and simple to use)
- Redis (for event-driven communication)
- Kafka (for high-performance streaming)
- NATS (lightweight and cloud-native messaging)
- RabbitMQ (message queuing for asynchronous tasks)
NestJS makes building microservices efficient and scalable with its built-in support for various transport mechanisms and modular architecture. Whether you are handling inter-service communication via TCP, Redis, or Kafka, NestJS provides a robust foundation for developing microservices in Node.js.
🚀 Start building your microservices with NestJS today!
